What is Eczema?
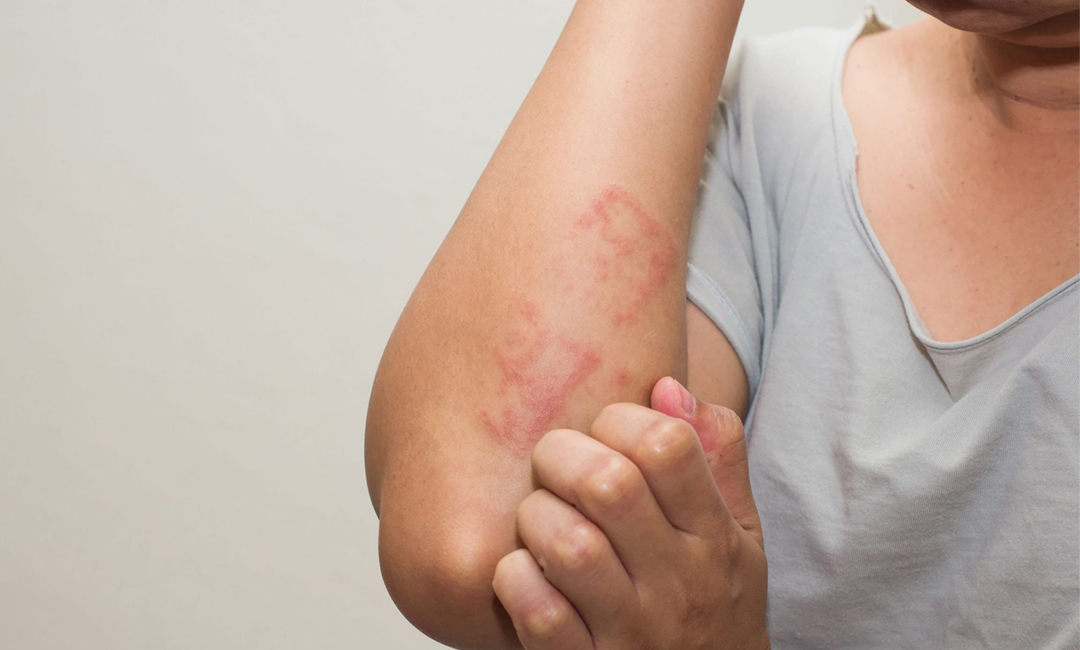
Eczema is a condition where patches of skin become inflamed, red, itchy, cracked and rough and sometimes blisters may also occur. Eczema can be a frustrating skin condition when you have to deal with it a few times a year or sometimes every day. It is very important to work closely with your doctor to make plans to help control the rashes and itchiness.
Eczema begins as red, raised tiny blisters containing a clear fluid atop red, elevated plaques. The affected skin will weep and ooze when the blisters break. In older eczema or chronic eczema, the blisters are less prominent and the skin is scaled, elevated and thickened. It is almost always itchy.
Eczema is common in children but can also occur to any age groups. Atopic dermatitis is chronic and tends to flare periodically.
Symptoms of Eczema or Atopic Dermatitis
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis can vary depending upon the age of the person. It commonly occurs in infants with dry and scaly patches appearing on the skin. These patches often itch intensively.
The most common symptoms of eczema include:
- Dry skin;
- Itching, which may become severe at night;
- Small, raised bumps which may also leak fluid and crust over when scratched;
- Raw, sensitive and swollen skin from scratching;
- Thickened, cracked and scaly skin;
- Red to brown-grey patches on the skin especially on feet, ankles, hands, neck, wrists, upper chest, eyelids and face and scalp of infants.
Atopic dermatitis often begins to develop before the age of 5 and may persist to adolescence and adulthood. For some people, it spreads periodically and then clears up for a time, even for several years.
Causes and Risk Factors of Eczema
The specific causes of eczema remain unknown but it is believed to be developed due to environmental or genetic factors. Healthy skin retains moisture and protects it from bacteria, allergens and irritants. Eczema is related to a gene variation that affects the skin’s ability to provide this kind of protection. It allows your skin to be affected by environmental factors, allergies and irritants.
Food allergies may also cause eczema in some children.
The primary risk factor for atopic dermatitis is having a personal or family history of eczema, hay fever, allergies or asthma.
Facts on Eczema
- Certain foods such as nuts and dairy products can trigger the symptoms of eczema.
- Symptoms can vary depending on the age of the person, but they often include scaly, itchy patches of skin.
- Eczema can also be triggered by environmental factors like smoke and pollen.
- A complete cure for eczema has not been found yet and usually, the treatment focuses on healing the damaged skin and alleviating symptoms.
- It is not a contagious condition.

Treatment for Eczema
There is no cure for eczema! Treatment only aims to heal the affected skin and prevent flare-ups of the symptoms. Usually, doctors suggest a plan for the treatment based on the person’s age, symptoms and current health condition. There are medical products for eczema that relieves from its symptoms and cures the affected skin.
For some people, eczema goes away over time. For others, it remains a lifelong condition.
Some Home Care Remedies Include
Along with the on-going medications, there are numerous things that can be done to support skin health such as:
- Taking lukewarm baths
- Applying moisturizer within 3 minutes of bathing.
- Wearing soft cotton fabrics and avoiding rough, scratchy fabrics and tight-fitting clothes.
- Using a mild soap or non-soap cleanser while washing.
- Try to avoid rapid changes in weather and the activities that make you sweat.
- Using a humidifier in dry or cold weather.
- Keep the fingernails short to prevent scratching.
Medical Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis
There are several products like Tacroz tacrolimus ointment 0.1% which is used to relieve from the symptoms of atopic dermatitis. Tacroz forte is a standard generic tacrolimus ointment manufactured by Glenmark. The ointment was approved for the treatment of eczema in December 2000.
Tacrolimus in the ointment suppresses the immune system and the inflammation by hindering an enzyme essential for the multiplication of T-cells, the cells that are required for the activation of the immune system. It generally takes a period of about 6 weeks to show noticeable results.
After alleviating the symptoms, use Demelan cream, to treat the discolouration caused by eczema.